Ethiopia is a land of ancient history, breathtaking landscapes, and vibrant cultures. When exploring the quality of life here, there's a mix of contrasting elements that paint a vivid picture of everyday living. From bustling city streets to serene rural communities, Ethiopia offers diverse experiences.
Living conditions vary greatly depending on location. In cities like Addis Ababa, you find a blend of modern infrastructures like shopping centers and traditional markets, whereas rural areas often depict a more laid-back lifestyle grounded in agriculture. Understanding the cost of living in these different settings is crucial for anyone considering a move or extended stay.
Healthcare and education systems in Ethiopia present a blend of public and private services. While advancements have been made, there are still areas that require development. Yet, the country's commitment to improving these sectors is evident through ongoing projects and international collaborations.
Culture and social life in Ethiopia are rich and diverse. The nation boasts numerous festivals, traditional music, and cuisine that reflect its deep-rooted heritage. Whether you're exploring ancient churches in Lalibela or participating in the vibrant Timkat festival, the cultural experience here is immersive and memorable.
If you're planning to visit or move to Ethiopia, some essential travel tips include understanding local customs, embracing the hospitality, and being mindful of safety practices. Navigating this beautiful country becomes easier and more enriching with a bit of preparation and an open heart.
- Living Conditions and Cost of Living
- Healthcare and Education
- Cultural and Social Life
- Travel Tips and Safety
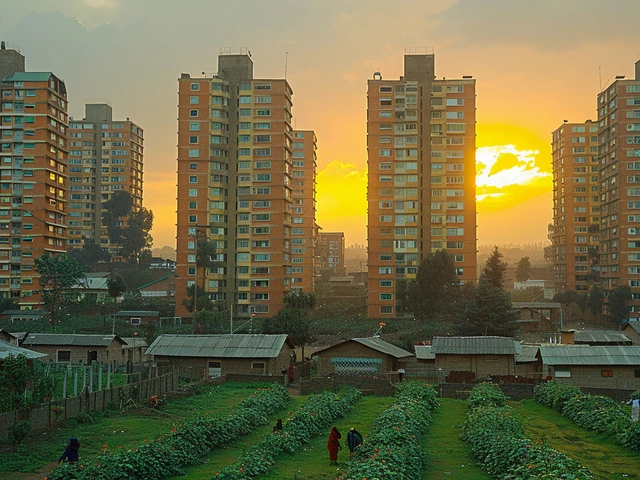
Living Conditions and Cost of Living
Delving into the living conditions in Ethiopia, one quickly notices the striking differences between urban and rural areas. In cities such as Addis Ababa, there is a bustling urban life with various modern amenities. The city is home to numerous international businesses, upscale restaurants, and shopping malls. However, it also retains a unique charm with its traditional markets, where locals buy fresh produce and handmade crafts, creating a quaint juxtaposition of modern and traditional Ethiopian lifestyles.
Renting an apartment in Addis Ababa can be relatively affordable compared to many Western cities, but it's crucial to consider various factors. For example, while a modern, furnished one-bedroom apartment in the city center might cost around $500 per month, the same apartment outside the central area could be as low as $200. This significant difference offers prospective residents flexibility based on their budget and preference for proximity to the city center. In contrast, rural areas offer a simpler, more affordable lifestyle where agriculture is the primary livelihood, making accommodation and living costs considerably cheaper.
Another important aspect to ponder is the cost of everyday goods and services. In Addis Ababa, dining out at a mid-range restaurant for two might set you back about $15. Essential groceries such as bread, milk, and rice are relatively inexpensive, often totaling up to $100 for a month's supply. Public transportation in the city is primarily covered by reasonably priced buses and minibuses, with a monthly commute pass costing around $20. Additionally, utility costs like electricity and water are quite affordable, typically averaging $50 per month, making day-to-day living manageable for various income levels.
Rural living conditions in Ethiopia offer a different experience. Here, life progresses at a slower pace, with communities deeply rooted in agricultural activities. Though facilities like healthcare and education services are present, they may not be as developed as in urban settings. The cost of living is significantly lower, with most families growing their food, reducing dependence on external food supplies. Social structures in rural areas are close-knit, with communities often coming together to support each other during harvests, celebrations, and times of need.
In terms of housing, traditional Ethiopian homes in rural areas are known as tukuls, round huts made from mud, straw, and wood. Barring the construction materials and styles, these homes reflect a sustainable way of living, harmonizing with the environment. While this might appear rustic, it provides insight into the country's rich cultural heritage and practical lifestyle.
"Ethiopia's unique living conditions and affordable cost of living truly offer a profound look into a life that builds on strong community ties and sustainable practices," notes Dr. Lia Tadesse, Ethiopia's Minister of Health.
For expatriates or individuals considering moving to Ethiopia, understanding these contrasts is essential. Factors like location, lifestyle preferences, and income levels influence the overall experience. By embracing the diversity present in different regions, one can enjoy the benefits of both urban's vibrant energy and rural's serene simplicity. These elements combined paint a comprehensive picture of Ethiopia's living conditions and costs, illustrating a nation rich in culture and varying lifestyles.

Healthcare and Education
In Ethiopia, healthcare and education are two areas of significant focus by both the government and international organizations. These sectors are crucial for enhancing the quality of life and driving long-term development. Over recent years, there have been notable advancements, though challenges remain.
Healthcare in Ethiopia has undergone substantial progress. The country operates a tiered healthcare system designed to provide comprehensive services starting from basic care at health posts to more advanced treatments at specialized hospitals. However, the distribution of facilities remains uneven, favoring urban areas. Addis Ababa, for instance, boasts several well-equipped hospitals such as the Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, known for its comprehensive range of medical services. In contrast, rural areas often rely on health centers and clinics that may face resource constraints.
One of the critical milestones for the Ethiopian healthcare system has been the significant reduction in child mortality rates. Between 2000 and 2020, under-five mortality dropped by more than half. This was largely attributed to increased immunization coverage, improved maternal health services, and better access to clean water and sanitation. Moreover, the country has been making strides in combating diseases such as malaria and tuberculosis through targeted public health initiatives.
The healthcare workforce in Ethiopia is supported by the government’s emphasis on training and deploying health professionals. The Health Extension Program, which trains women as community health workers, has been particularly impactful. These workers play a vital role in providing preventive and basic curative services to their communities. However, there remains a need for more specialists and improvements in healthcare infrastructure to meet growing demands.
Ethiopian Minister of Health, Dr. Lia Tadesse, stated, "Investing in health systems is investing in our future. Our goal is to build a resilient healthcare system that can serve all Ethiopians effectively."
Education in Ethiopia is a dynamic sector making significant headway despite historical challenges. The country follows a 4-4-2 system: four years of primary education, followed by four years of intermediate education, and two years of preparatory education leading up to university entrance. In recent years, efforts to increase enrollment rates have been successful, particularly at the primary level. The government has introduced measures such as building more schools and employing additional teachers, especially in underserved areas.
Higher education is also evolving, with numerous universities across the country offering a wide range of programs. Institutions like Addis Ababa University are at the forefront, providing undergraduate and postgraduate courses in diverse fields. While access to tertiary education has improved, challenges such as resource limitations, overcrowded classes, and the need for more qualified educators persist. Technical and vocational education is also emphasized, aiming to equip students with practical skills relevant to the job market.
Efforts to enhance the quality of education include curriculum reforms and investments in educational technology. However, factors like poverty, gender disparity, and regional inequalities pose hurdles. Programs targeting these issues, such as scholarships for girls and initiatives promoting inclusive education for children with disabilities, are crucial steps towards more equitable education.
In summary, healthcare and education systems in Ethiopia are on a path of improvement, marked by dedicated efforts and significant achievements. While there is still a journey ahead to address the existing challenges, the commitment and progress observed offer a hopeful outlook for the future.

Cultural and Social Life
One of the most captivating aspects of Ethiopian culture is its deep historical roots and vibrant traditions. Ethiopians are immensely proud of their heritage, which can be seen through their customs, festivals, and daily interactions. A major highlight is the ancient town of Lalibela, famous for its rock-hewn churches. These structures, carved out of solid rock in the 12th century, are not only architectural marvels but also significant religious sites, drawing visitors and worshippers alike.
Music and dance play a crucial role in everyday life. Traditional music, often characterized by unique rhythms and instruments such as the masenqo (a one-string fiddle) and the krar (a lyre), is central to many social and religious events. One cannot discuss Ethiopian music without mentioning the country’s jazz scene, which blossomed in the mid-20th century and continues to influence global jazz artists.
The country's festivals are colorful and lively celebrations, each with its unique significance. Timkat, the Ethiopian Epiphany, is perhaps the most spectacular, attracting thousands of people who participate in religious processions, prayers, and communal feasting. Another notable event is Meskel, commemorating the discovery of the True Cross, which involves lighting massive bonfires and vibrant parades.
Ethiopian cuisine is another window into the country's rich cultural landscape. Central to the cuisine is injera, a sourdough flatbread with a slightly spongy texture, which serves as the base for many meals. Dishes like doro wat (spicy chicken stew) and kitfo (minced raw beef) are accompanied by injera and a variety of side dishes made from lentils, vegetables, and spices. The communal aspect of dining, where everyone shares from a common plate, underscores the importance of community and togetherness in Ethiopian culture.
Social life in Ethiopia often revolves around strong community ties and familial bonds. Ethiopians are known for their hospitality and warmth, often inviting strangers into their homes for coffee, which holds a sacred place in the culture. The traditional coffee ceremony is a time-honored practice that involves roasting and brewing coffee beans, often taking several hours, signifying friendship and respect.
Languages provide another layer of cultural richness. While Amharic is the official language, Ethiopia is home to around 80 different languages and numerous dialects, each representing different ethnic groups. This linguistic diversity is a testament to the country's complex cultural fabric.
The influence of ancient traditions is balanced by modern social trends, particularly in urban areas. Cities like Addis Ababa boast a burgeoning art scene, with numerous galleries and cultural centers showcasing contemporary Ethiopian artists. The city's nightlife, with its blend of traditional music venues and modern clubs, offers a glimpse into the evolving social dynamics.
"Ethiopia possesses a unique cultural heritage, stretching back over 3,000 years, with numerous significant archaeological discoveries, including the fossil of one of early humans, known as 'Lucy.'" - UNESCO

Travel Tips and Safety
Traveling to Ethiopia can be an exciting adventure, given its rich history, stunning landscapes, and unique cultural experiences. However, to make the most of your trip and ensure your safety, it’s important to be well-prepared. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind when traveling to this fascinating country.
First and foremost, understanding and respecting local customs is vital. Ethiopians are often very hospitable, and they value politeness and respect. When entering someone's home, it’s customary to remove your shoes. Greetings usually involve a handshake, and men often touch shoulders three times. Learning a few basic phrases in Amharic, the national language, such as “Selam” (hello) and “Ameseginalehu” (thank you), can go a long way.
Another key aspect is staying healthy. Ethiopia has both private and public healthcare facilities, but it’s advisable to bring any necessary medications with you, as availability of specific drugs may vary. Drinking bottled or filtered water is recommended to avoid waterborne illnesses. Many travelers opt to carry hand sanitizer and drink only from sealed bottles. Before traveling, make sure your vaccinations are up-to-date, and consult your healthcare provider about any additional vaccines you might need.
When it comes to transportation, Ethiopia offers a range of options from taxis to buses and even bajajs, which are three-wheeled motorcycles. While public transport can be an affordable way to get around, it might not always be the most reliable. Taxis are a better option for comfort and safety, especially if they are booked through reputable services. If you decide to rent a car, be wary of road conditions and local driving habits, which can be quite different from what you might be used to.
Safety is always a concern for travelers, and in Ethiopia, certain precautions can help ensure a safe trip. It’s advisable to avoid traveling at night, particularly in rural areas, and always stay aware of your surroundings. Petty theft can occur in busy markets and tourist areas, so keeping your belongings secure is essential. Carrying a copy of your passport, rather than the original, and storing valuables in a hotel safe can reduce the risks.
Emergency preparedness is another critical component. Familiarize yourself with the local emergency numbers and the location of your country’s embassy. In case of any emergencies, such as natural disasters or civil unrest, having a plan and knowing where to go can make a big difference. It’s also a wise idea to register with your embassy upon arrival so that you can receive timely updates and assistance if needed.
When planning your itinerary, consider the diverse climate zones in Ethiopia. From the highlands to the lowlands, temperatures and weather conditions can vary greatly. Packing layers and appropriate clothing for different climates ensures that you’re comfortable throughout your journey. Also, some regions are more prone to malaria, so using mosquito repellent and sleeping under mosquito nets are practical measures to protect yourself.
Finally, always be culturally sensitive and conscious of your behavior. Many historical sites, such as the rock-hewn churches of Lalibela, are also places of worship. Dressing modestly and following guidelines set by locals shows respect. Taking photos without permission can be considered rude, especially in rural areas.
Traveling in Ethiopia is a rewarding experience that offers much to see and learn. By staying informed and prepared, you can ensure your visit is both safe and enjoyable, creating memories that will last a lifetime.
 Exploring Housing in Ethiopia: Types, Costs, and Living Conditions
Exploring Housing in Ethiopia: Types, Costs, and Living Conditions
 Dentist Salary in Ethiopia: Earnings, Insights, and Opportunities
Dentist Salary in Ethiopia: Earnings, Insights, and Opportunities
 Understanding Poverty in Ethiopia: Facts and Insights
Understanding Poverty in Ethiopia: Facts and Insights
 Profitable Business Opportunities in Ethiopia
Profitable Business Opportunities in Ethiopia
 Profitable Business Opportunities in Ethiopia: Exploring Lucrative Ventures in 2024
Profitable Business Opportunities in Ethiopia: Exploring Lucrative Ventures in 2024
love monster
July 9, 2024 AT 17:44Great overview of Ethiopia's quality‑of‑life index, especially the contrast between urban and rural socio‑economic stratification. The breakdown of housing costs in Addis Ababa versus the tukul lifestyle really highlights the trade‑offs for expatriates. I’d add that renewable energy initiatives are gradually influencing utility pricing, which could shift those numbers over the next decade. Overall, solid groundwork for anyone interested in a deep dive.
Christian Barthelt
July 11, 2024 AT 11:26Minor nitpick: the article uses "healthcare" as two words in a few places; the standard term is "healthcare" (single word). Also, the phrase "a bit of preparation" would read better as "some preparation".
Ify Okocha
July 13, 2024 AT 06:30The piece glosses over the glaring deficiencies in rural health infrastructure, treating them as mere footnotes. While urban hospitals receive praise, the chronic understaffing in peripheral clinics remains a systemic failure. Ignoring these disparities does a disservice to readers seeking a realistic assessment.
William Anderson
July 15, 2024 AT 01:50One must commend the author for attempting a panoramic view, yet the narrative collapses under pretentious verbosity. Describing tukuls as "sustainable architectural marvels" feels forced when basic sanitation is still lacking. The dramatics around "vibrant energy" ignore the fact that power outages are frequent. A more balanced tone would serve the subject better.
Sherri Gassaway
July 16, 2024 AT 20:53When we contemplate the essence of community, we must ask whether modernity erodes the very soul that defines Ethiopian hospitality. The coffee ceremony, for instance, is not merely a ritual but a metaphysical bridge between generations. Yet, the article skims past this depth, treating culture as a checklist. Perhaps a deeper ontological inquiry is warranted.
Milo Cado
July 18, 2024 AT 16:13Thank you for this comprehensive guide; it truly encapsulates the multifaceted nature of life in Ethiopia. The way you delineated the cost of living in Addis Ababa versus rural areas offers clear, actionable data for prospective residents. I particularly appreciate the inclusion of specific figures-such as the $500 monthly rent for a downtown apartment-since abstract ranges often leave readers guessing.
In the healthcare section, highlighting both the advances in urban hospitals and the challenges faced by health posts paints an honest picture of the system’s duality. The discussion of the Health Extension Program underscores the importance of community health workers, an aspect that deserves more international attention.
Your cultural analysis shines when describing festivals like Timkat, capturing the vibrancy and communal joy that define Ethiopian celebrations. The emphasis on the coffee ceremony as a social glue further illustrates how everyday practices reinforce societal bonds.
The travel tips are both practical and considerate. Advising travelers to carry copies of passports and avoid nighttime travel in rural zones reflects a deep understanding of safety nuances. Moreover, the suggestion to learn basic Amharic phrases demonstrates cultural respect that can enrich any visitor’s experience.
Throughout the article, your balanced tone-neither overly romanticizing nor unduly critical-offers readers a nuanced perspective. The optimism you convey, especially regarding ongoing development projects, inspires confidence in Ethiopia’s future.
Overall, this piece serves as an exemplary template for destination guides, combining factual rigor with cultural empathy. 😊
MONA RAMIDI
July 20, 2024 AT 11:33This write‑up feels flat and uninspired, barely scratching the surface of Ethiopia’s rich tapestry. If you’re going to call it a guide, it should at least capture the drama of daily life!
grace riehman
July 22, 2024 AT 06:53Nice article! I likey how u breaked down the cost stuff and the cultuar bits. It makes it easy 4 peopel who want to move.
Vinay Upadhyay
July 24, 2024 AT 02:13Oh, brilliant-another "comprehensive" overview that completely sidesteps the glaring issue of infrastructure decay. You mentioned "modern amenities" in Addis, yet you ignore the fact that traffic congestion can double commute times. And let's not forget the occasional typo: "health care" should be one word, as any grammar‑conscious reader will point out. Still, kudos for the generous sprinkling of emojis elsewhere-just wish the analysis matched that enthusiasm.